A brief history
The beginning: trade software for money
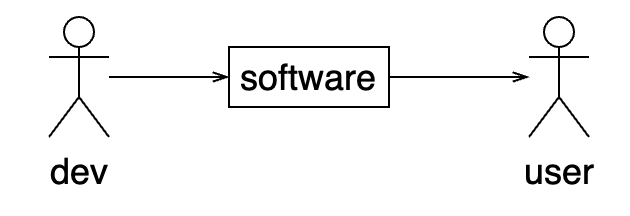
Distribution problems: installation, licensing, upgrades
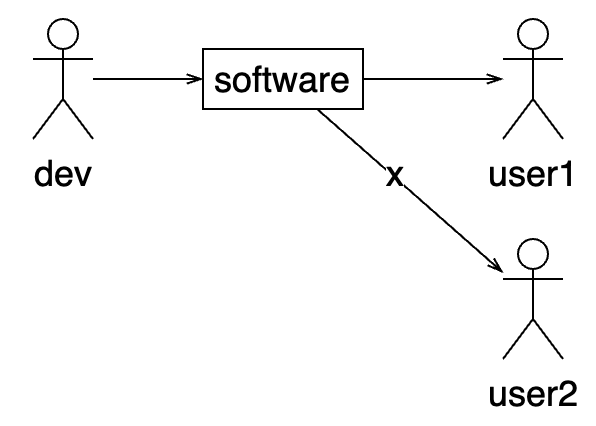
Client / Server
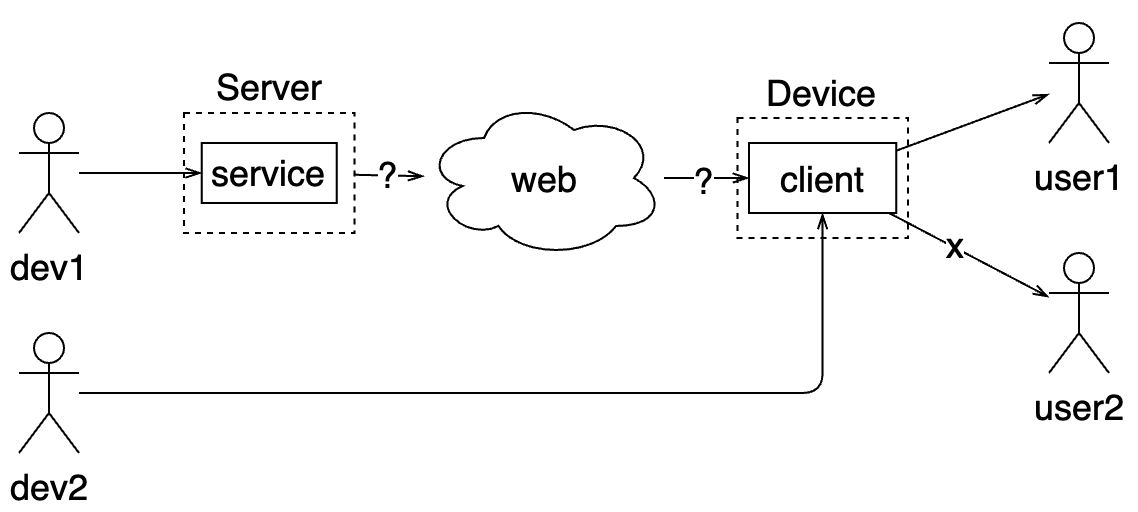
Distributed services (Conway’s law)
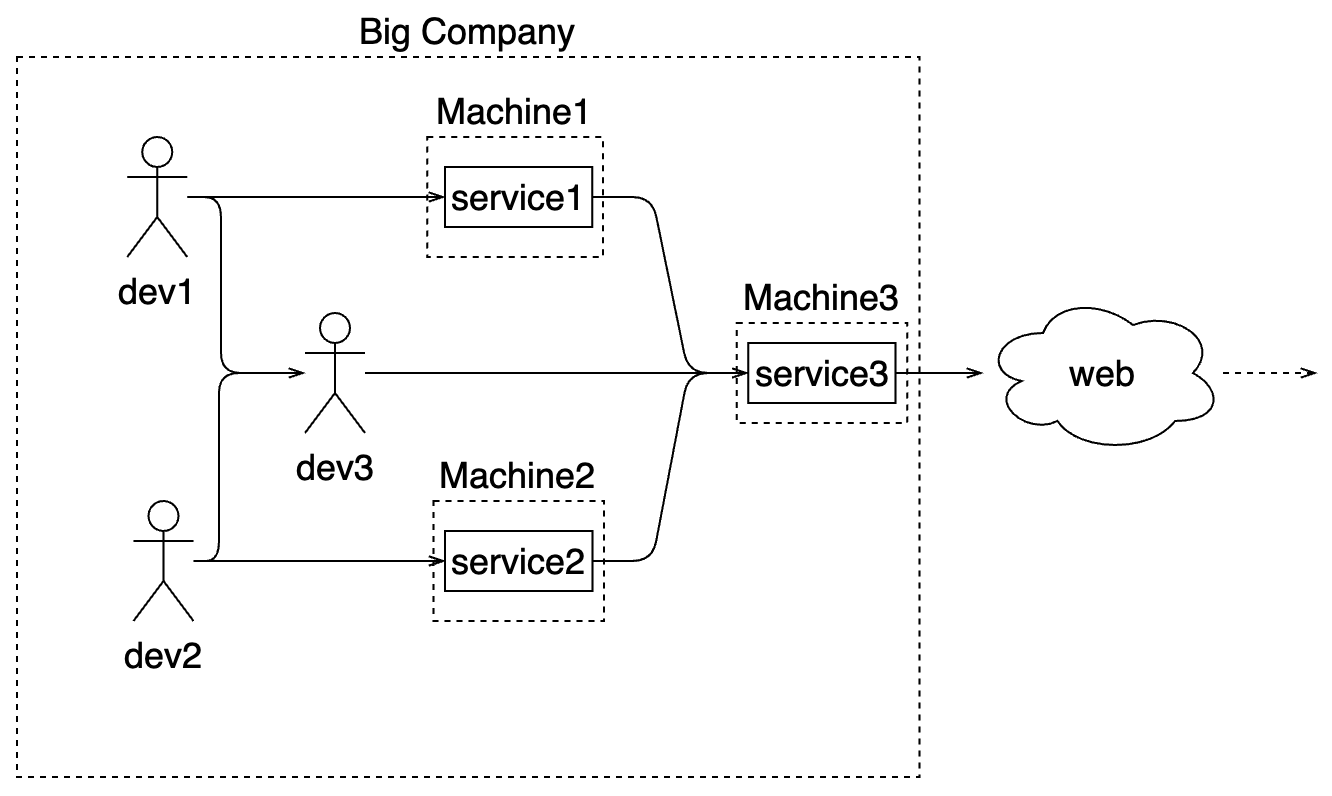
Exploiting resources: Andy and Bill’s law
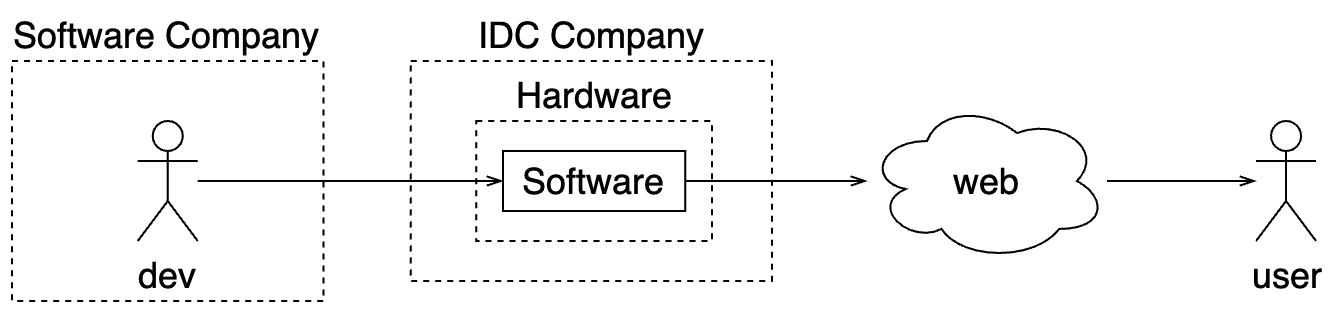
Outsourcing hardwares
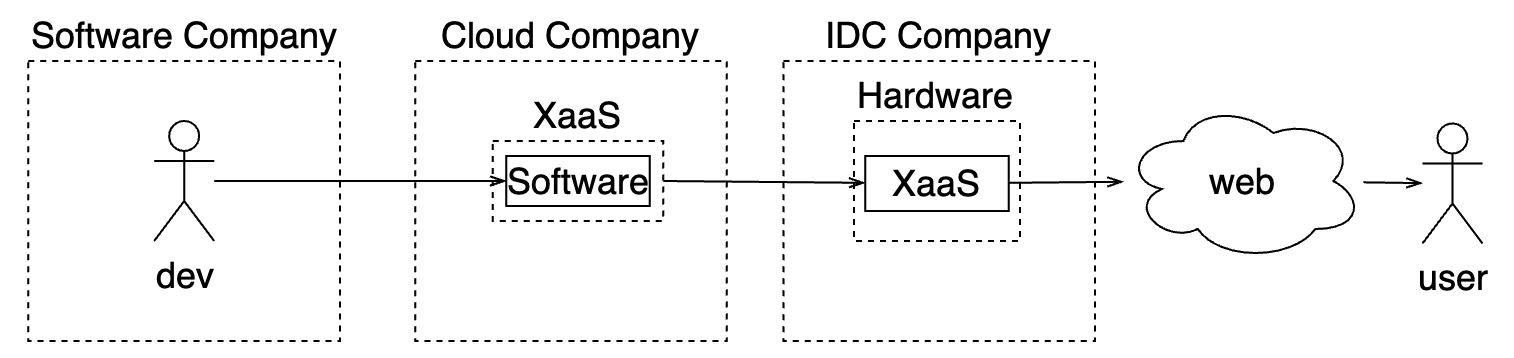
Outsourcing Infra-Softwares
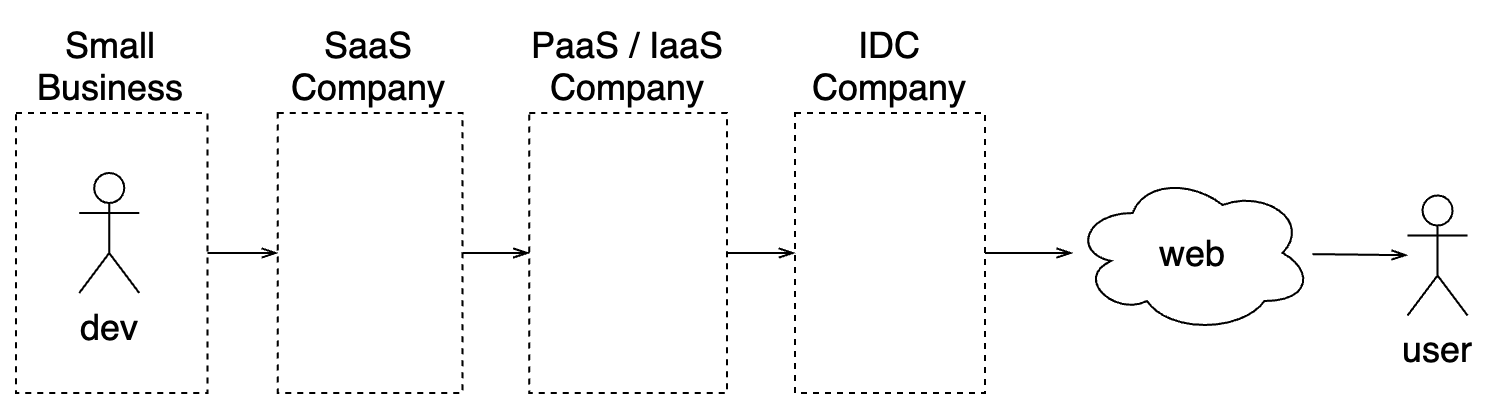
Cloud industry
Software delivery concept evolution (SWOT analysis)
| Concept | strength | weakness | opportunity | threat |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| library | extension and consolidation | requires build; cannot deploy independently | semantic versions | dependency hell; backward / forward compatibility |
| runtime binary + scripts | deploy independently; cross-platform; | slow; cannot conceal information; need a large runtime to do small things | fast development | hard to maintain; cannot hide sensitive information |
| binary packages / installers | does not require build; has more complexity | cannot cross-platform; cannot fully control the deployment environment | sell as products, license and fee | hard to upgrade; security risks. |
| services on servers | more control on the deployment sites; upgrade anytime | performance / experience depends on network connections | APIs; social networks; zero down time; freeminum | network security; do not control client upgrades |
| distributed / tiered services | independent deployment and evolution, divide and conquer | coupled with the human structure (Conway’s law) | business can hire more people | single point of failure; service explosion and governance; inconsistency |
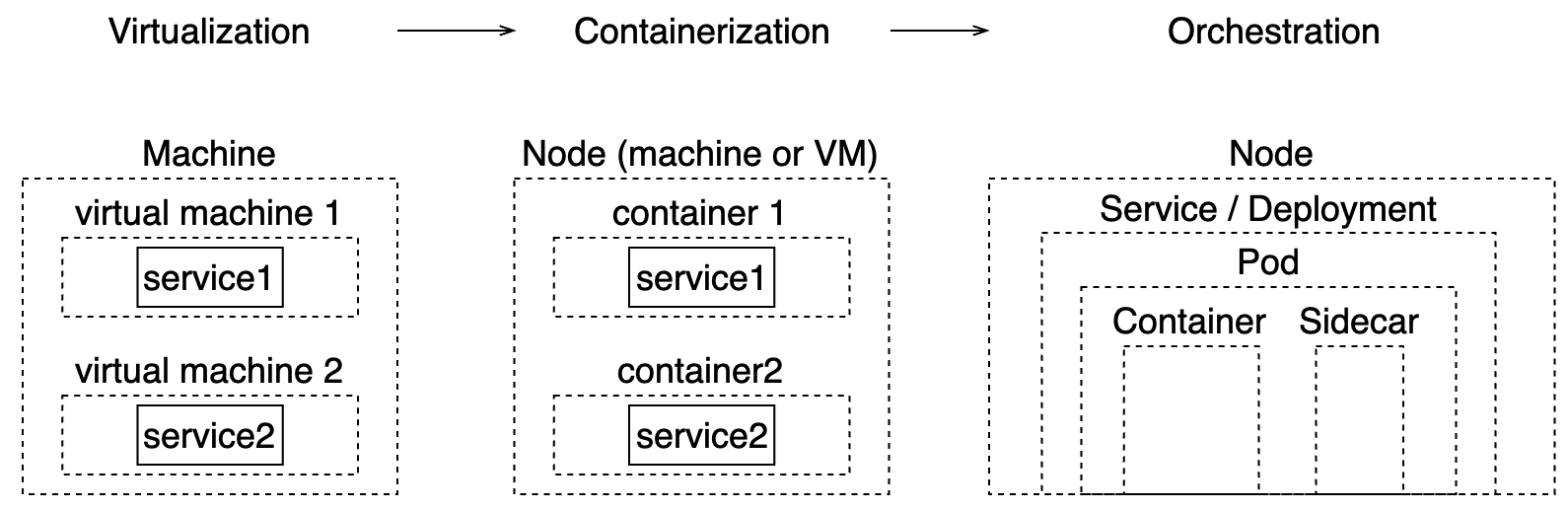
| virtualization | higher efficiency on hardware resources | start / stop is slow (in minutes) | scale up and down; pay as you go | more security loopholes |
| containerization | a new interface to deliver and run software fast and cheap | docker / containerd dependency; loss of observability and performance; | docker image repos; CI / CD | docker vendor turf wars |
| container orchestration | container operations | still need to maintain nodes | multi-tenancy container clusters; sidecars | vendor lock-in on k8s designs and cloud providers; too many yamls; loss of dev agility |
| service mesh | observability, network routing, more ways of load balancing and flow control | more network hops and latencies; over design for most systems; | chaos engineering, system-level performance testing | Sidecar errors may be a single point of failure |
| Serverless | divide between functional and non-functional requirements | reinventing PaaS; maybe a wrong division; hard to work on special non-functional requirements. | low-code, no-code: faster development with less qualified developer. | too many hidden layers; vendor lock-in |
| IDC | outsourcing hardwares | performance dependent on IDC connections and power supply | multi-region availability; CDN; pay as you go on hardware layer. | data security; cannot evolve on hardware / software integrations |
| Cloud | outsourcing softwares and system operations | system has more hidden layers | easy infrastructure; pay as you go on more layers; no need to maintain hardwares | vendor lock-in; Hotel California pricing |